leaking
This is what the challenge looks like, there's a python script and the output attached with the challenge.
Let's take a look at the python script and the output.
from Crypto.Util.number import *
with open('flag.txt') as f:
flag = f.read().strip()
p = getPrime(512)
q = getPrime(512)
n = p * q
phi = (p - 1) * (q - 1)
e = 65537
d = inverse(e, phi)
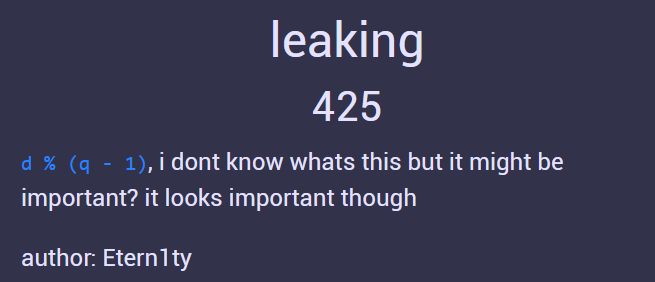
hmmm = d % (q - 1)
ct = pow(bytes_to_long(flag.encode()), e, n)
with open('output.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write(f'n = {n}\n')
f.write(f'ct = {ct}\n')
f.write(f'hmmm = {hmmm}\n')
n = 107608865796252607787589478940986641645492239450169703491031326268140692492372510892367061938730408456806020895432357325849349810482561504370583158335934698827409694378188622297732258055410289374082538108727963882298404546595204093800594588293861626737088348911289744141235659586256512579993240423711215700743
ct = 47178680209035556203882073442096371534276865857451504400445557317612379506778804434473745409774809280598269803385381897423027589220081058331514035778607710662431683007211584463701427831933579399764891935726815516956174999080394629247885665815679463055813266447661747510400318305201324386503391989412078674602
hmmm = 2545803641186215531176976231380080814510536759970800033204052622078895877272323130104777431775690959615730074427330141463544010753787206871967852996718673
So, the python scripts generates a 1024-bit RSA modulus n = p * q, uses public exponent e = 65537, computes the private exponent d = e^{-1} mod phi(n), and then outputs the ciphertext ct = m^e mod n and the value hmmm = d mod (q-1).
We know d satisfies:
e * d ≡ 1 (mod (p-1)(q-1))
But the program leaked only hmmm = d mod (q-1). This gives a congruence modulo q-1:
d ≡ hmmm (mod q-1)
Multiply both sides by e:
e * d ≡ e * hmmm (mod q-1)
Since e * d ≡ 1 (mod q-1) (because e*d ≡ 1 (mod (p-1)(q-1)) implies the congruence modulo any divisor such as q-1), we get
1 ≡ e * hmmm (mod q-1)
Therefore
q - 1 | (e * hmmm - 1)
Let
k = e * hmmm - 1
So q - 1 divides k (i.e. k = t*(q-1) for some integer t). This means for any integer a coprime to q we have by Fermat/Euler-like reasoning:
a^k ≡ a^{t*(q-1)} ≡ 1 (mod q)
Thus a^k - 1 is a multiple of q. Computing g = gcd(a^k - 1, n) therefore often yields q (or p), because g shares q as a common factor with n while typically being smaller than n.
This is the crux of the attack: compute k = e*hmmm - 1 and attempt g = gcd(a^k - 1, n) for small values of a (e.g., 2, 3, 5...). If 1 < g < n, then g is a nontrivial factor of n (either p or q).
This is the step by step of our attack :
- Compute
k = e * hmmm - 1wheree = 65537. - For small bases
a(2, 3, 5, 7, 11, ...), computeg = gcd(a^k - 1, n). - If
1 < g < n, thengis a prime factor (eitherporq). Compute the other factorn // g. - Compute
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)and recover the private exponentd = e^{-1} mod phi. - Decrypt
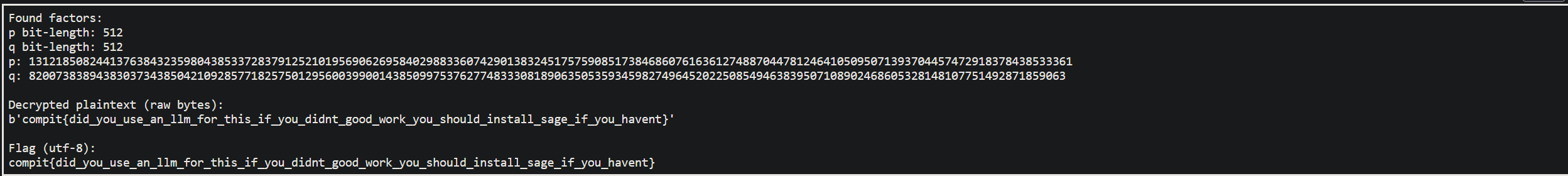
ctwithdto retrievem = ct^d mod nand convert to bytes to obtain the flag.
You can check out the attack script here and try it yourself
PO- PO- PO- PWNED!